Java inheritance promotes reusability and polymorphism, supporting single, multilevel, hierarchical inheritance and interfaces.
Introduction to Inheritance in Java
Inheritance in Java is a core concept in object-oriented programming (OOP) that enables a class (known as a subclass or derived class) to inherit properties and behaviors (fields and methods) from another class (known as a superclass or base class). This powerful feature helps developers build modular, readable, and reusable code. In simpler terms, when one class acquires the properties of another class, it’s called Inheritance in Java program.
Importance and Advantages of Inheritance in Java
1. Code Reusability:
Subclasses reuse code from the superclass without rewriting it.
Example: Car class can reuse properties from Vehicle.
2. Modularity:
Java inheritance promotes a modular and structured approach.
Helps in breaking the problem into manageable pieces.
3. Polymorphism in Java:
Inherited classes can be used in a polymorphic way.
Supports Java polymorphism by allowing function overriding in Java.
4. Maintainability:
Inheritance allows easier updates and bug fixes.
Updating a method in the superclass reflects in all subclasses.
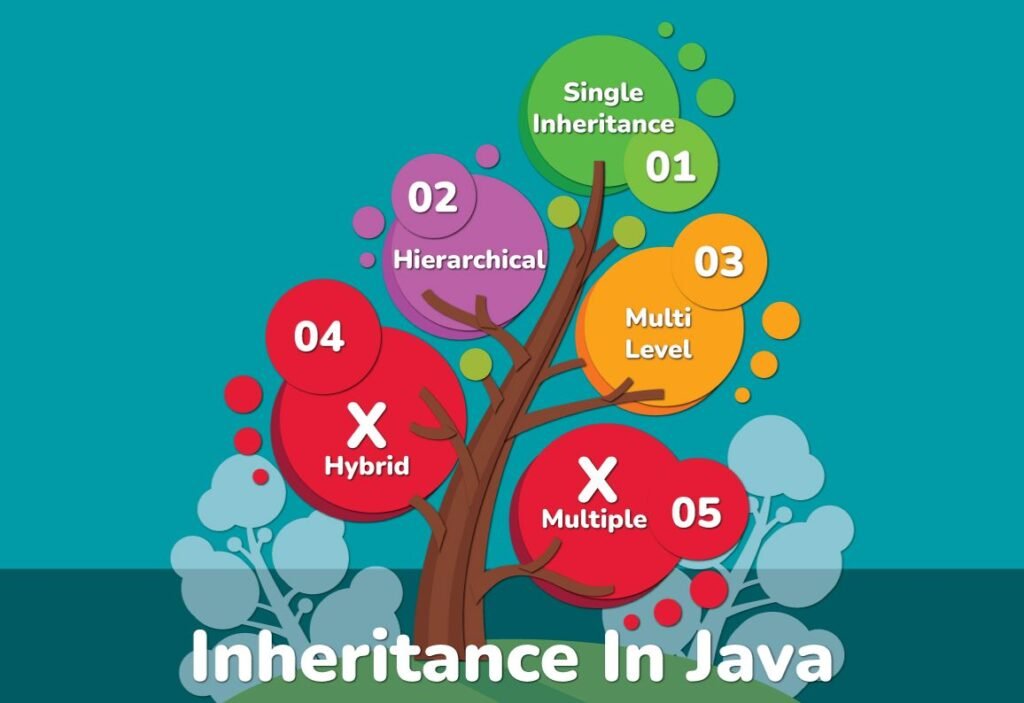
Types of Inheritance Supported by Java
1. Single Inheritance in Java
Java supports single inheritance, where one class inherits from a single superclass.
// java single inheritance program
class Vehicle {
void start() {
System.out.println(“Vehicle started.”);
}
}
class Car extends Vehicle {
void drive() {
System.out.println(“Car is being driven.”);
}
}
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Car car = new Car();
car.start();
car.drive();
}
}
2. Multilevel Inheritance in Java
When a class inherits from another class, which itself inherits from another class.
// multilevel inheritance in java
class Animal {
void eat() {
System.out.println(“Animal is eating.”);
}
}
class Dog extends Animal {
void bark() {
System.out.println(“Dog is barking.”);
}
}
class BullDog extends Dog {
void guard() {
System.out.println(“Bulldog is guarding.”);
}
}
3. Hierarchical Inheritance in Java
In this type, multiple subclasses inherit from a single superclass.
// hierarchical inheritance in java
class Shape {
void draw() {
System.out.println(“Drawing a shape.”);
}
}
class Circle extends Shape {
void draw() {
System.out.println(“Drawing a circle.”);
}
}
class Rectangle extends Shape {
void draw() {
System.out.println(“Drawing a rectangle.”);
}
}
4. Multiple Inheritance in Java
Java does not support multiple inheritance through classes due to the diamond problem. However, it allows multiple inheritance via interfaces, a feature of interface inheritance in Java.
// difference between inheritance and interface in Java
interface Jumpable {
void jump();
}
interface Runnable {
void run();
}
class Athlete implements Jumpable, Runnable {
public void jump() {
System.out.println(“Athlete jumps.”);
}
public void run() {
System.out.println(“Athlete runs.”);
}
}
Please visit our website to know more:-https://cyberinfomines.com/blog-details/inheritance-in-java